Networks
How networks work.
Learn
- Intro: https://drewdevault.com/2016/12/06/A-broad-intro-to-networking.html
- #todo Beej's Guide to Network Concepts
- #todo Beej's Guide to Network Programming
- #todo TCP/IP Illustrated
- #todo https://pboyd.io/posts/udp
Terminology
- IP: Internet Protocol
- TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
- UDP: User Datagram Protocol
- DNS: Domain Name system
- LAN: Local Area Network
- WAN: Wide Area Network
- ISP: Internet Service Provider
- URL: Uniform Resource Locator
- NIC: Network Interface Card
- Overlay network: a network layered on top of another network.
Basics
IP addresses are used to identify computers connected to the internet. Ports are used to identify programs running on these computers. Many programs listen on "standard" ports, e.g. HTTP(S) servers listen on 80(443). See the list of common port numbers.
Packets are being delivered much like physical mail: the combination of an IP address and a port (like a house address and an apartment number) is used to find the destination.
See also What happens when you type google.com into your browser and press enter.
Layers
The OSI model:
- Physical (wires, Wi-Fi)
- Network (addresses, IP protocol)
- Transport (ports, TCP/UDP protocols)
- Application (HTTP, SSH, etc)
Sockets
A network socket is a communication endpoint for exchanging data between programs over the network. A socket address consists of a transport protocol (TCP/UDP), an IP address, and a port number.
CIDR notation
Classless Inter-Domain Routing
A compact representation of a subnetwork.
The "mask" suffix after / represents the number of significant bits, from left to right.
The smaller the mask, the more IP addresses are available.
a.b.c.d/32represents a single IP address (netmask255.255.255.255)a.b.c.d/24represents a range froma.b.c.0toa.b.c.255(netmask255.255.255.0)a.b.c.d/16represents a range froma.b.0.0toa.b.255.255(netmask255.255.0.0)a.b.c.d/8represents a range froma.0.0.0toa.255.255.255(netmask255.0.0.0)a.b.c.d/0represents the entire range of IPv4 addresses (netmask0.0.0.0)
Private network addresses:
10.0.0.0/8172.16.0.0/12192.168.0.0/16
For most purposes, /24 subnets are a reasonable choice.
DNS
Domain Name System, a phone book for the internet.
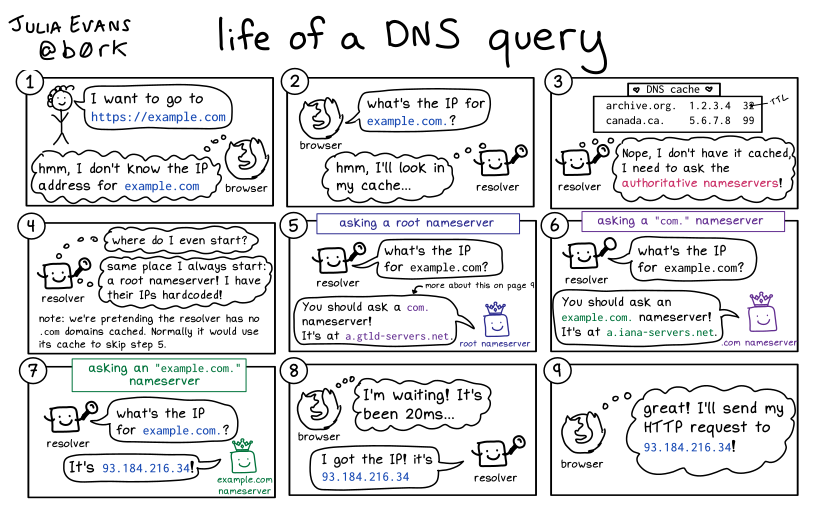
Learn:
- #todo https://messwithdns.net
- #todo https://jvns.ca/blog/2022/02/01/a-dns-resolver-in-80-lines-of-go
Record types:
- A for IPv4
- AAAA for IPv6
- CNAME for aliases
- MX for email
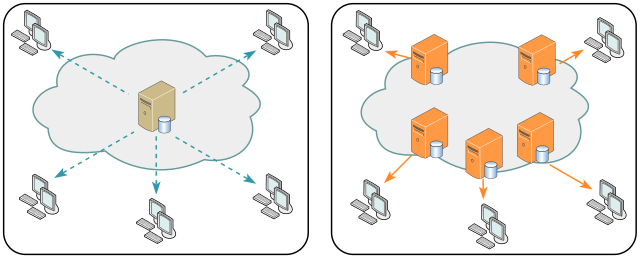
CDN
Content Delivery Network. A distributed network of servers that broadcasts web content to users. The servers are distributed around the world, significantly reducing delivery time compared to a single server.
Privacy
- Basic DNS + HTTP: ISP sees DNS requests and all traffic
- Basic DNS + HTTPS: ISP sees DNS requests, but traffic is encrypted with TLS
- DNS over TLS/HTTPS + HTTPS: ISP doesn't see DNS requests, but still sees IP address requests
- VPN: ISP sees nothing, all traffic including DNS requests goes through encrypted tunnel
Firewall
Tools:
iptables: firewall rules managerufw(uncomplicated firewall): user-friendly frontend foriptables
NAT
#todo https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_address_translation
P2P
#todo https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Peer-to-peer
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
A DHCP server dynamically assigns private IP addresses to devices on the local network. Its role is usually performed by the router.
PGP
PGP is a standard for E2E email encryption. GPG (GNU Privacy Guard) is a GNU's implementation of PGP.
Tools
- Wireshark: GUI packet analyzer